Advanced Features
Efficiency Curves
Some attributes in PyPES are not static metadata. For example, a Pump may have an efficiency curve rather
than a single efficiency value. To define an efficiency curve, first define a function and then use
set_pump_curve() to set the pump_curve attribute to that function. thermal_efficiency
and electrical_efficiency of Cogeneration and Boiler objects can be similarly defined.
from pype_schema.node import Pump
from utils import parse_quantity, PumpType, ContentsType
min_flow = parse_quantity(0, "gpm")
max_flow = parse_quantity(1000, "gpm")
avg_flow = parse_quantity(750, "gpm")
elevation = parse_quantity(10, "m")
horsepower = parse_quantity(100, "hp")
def efficiency_curve(flowrate):
return - (flowrate ** 2)
pump = Pump(
"PumpA",
ContentsType.UntreatedSewage,
ContentsType.UntreatedSewage,
min_flow,
max_flow,
avg_flow,
elevation,
horsepower,
1,
pump_type=PumpType.VFD
)
pump.set_pump_curve(efficiency_curve)
Currently, only static efficiency values are supported in the JSON format, but the long-term plan is to support dictionaries (through interpolation) and lambda functions.
Algebraic Mode
“Algebraic” mode involves the combination of operations are separated into binary (e.g., “+” or “-”) and unary (e.g., “∼” or “»”). Due to the closure of binary and unary operations, it is possible to recursively combine tags in any configuration the user desires. This allows for complex new data streams to seamlessly be integrated into system models.
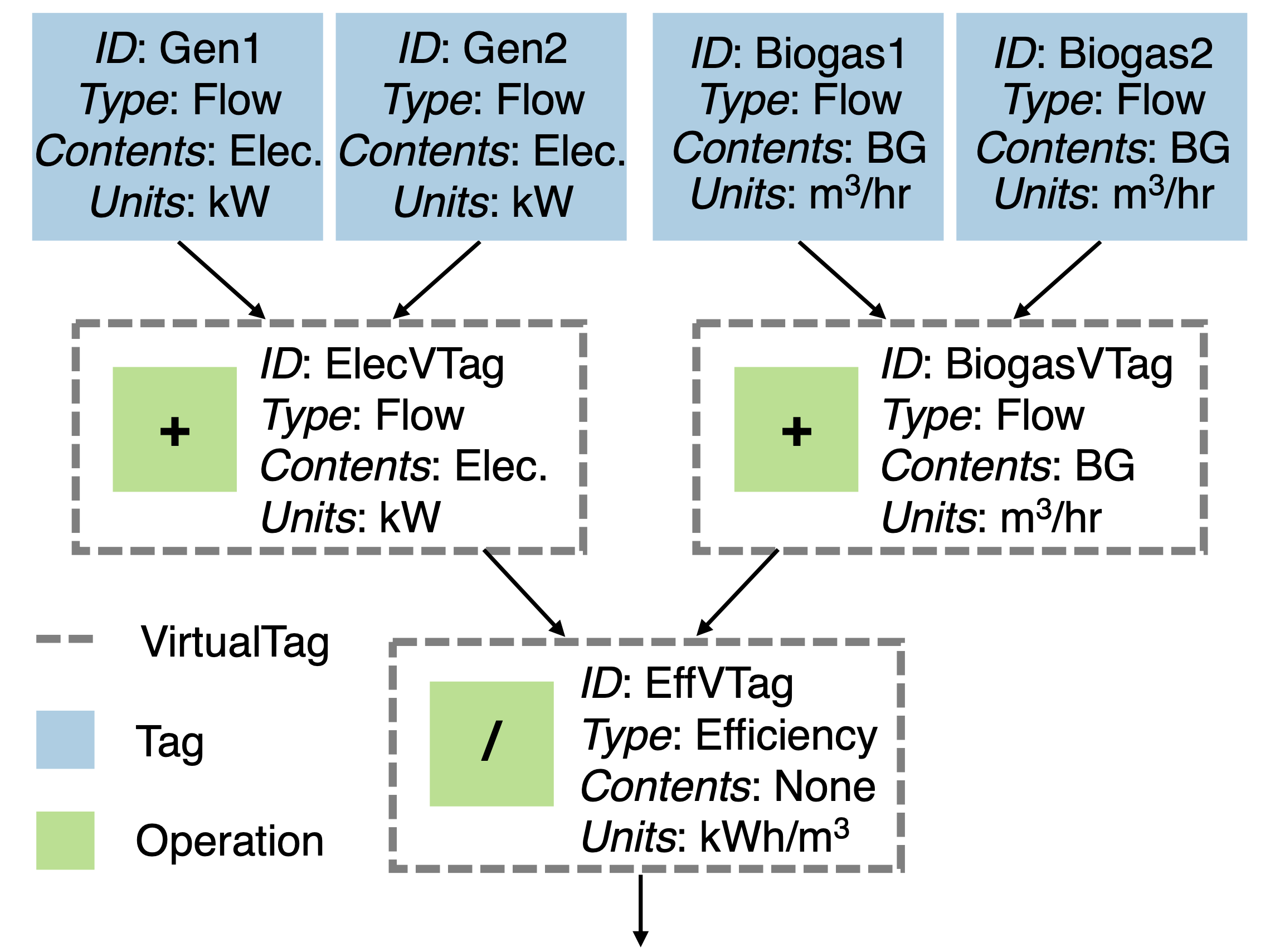
As an example, the figure below shows efficiency calculated by VirtualTag (“EffVTag”),
which is composed of two VirtualTag objects (“ElecVTag” and “BiogasVTag”) combined with the / operator.
VirtualTag objects “ElecVTag” and “BiogasVTag” are each a composition of two real-world sensor measurements using the + operator.
An example of how to define all the potential attributes in algebraic mode is available in wrrf_sample.json. A full table of supported algebraic operations can be found below. Proofs of operator closure will be published along with the PyPES manuscript, which is currently under peer review.
Operation |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
noop |
Unary operator |
No operation. Useful when skipping a tag in a list of unary operations |
delta |
Unary operator |
Input[t] - input[t-1] for t in 1,…,T |
<< |
Unary operator |
Shift all data to the left one timestep, so that the first timestep will be deleted from the data |
>> |
Unary operator |
Shift all data to the right one timestep, so that the last timestep will be deleted from the data |
- |
Unary operator |
Unary negation |
~ |
Unary operator |
Boolean negation. If numerical data, all nonzero values are changed to 0 and zeros to 1 |
+ |
Binary operator |
Addition |
- |
Binary operator |
Subtraction |
* |
Binary operator |
Multiplication |
/ |
Binary operator |
Division |
value |
Constant |
A value that is constant at all timesteps |
units |
Constant |
Dimensionality (e.g., cubic meters or kilowatts) |